
ANTI-COUNTERFEITING: THE BEST PROTECTION TECHNOLOGIES
Anti-counterfeiting does not just mean fighting the illegal action of international criminal gangs that profit from plagiarism without respecting borders and legality. Phenomena such as the black market, the gray market or Italian sounding threaten jobs and brand revenues alike. Technology helps companies protect products and consumers.
THE NUMBERS OF COUNTERFEITING TODAY
According to the researchers, the value of counterfeit imports into the EU exceeds 121 billion euros and involve the most diverse sectors: primarily cosmetics and toys, alcoholic beverages, electronics, clothing, chemicals and pharmaceuticals (Source: EUIPO / OECD 2020) . In addition to the issue of the protection of intellectual property and margins, anti-counterfeiting is an action due to consumers who, without the supervision and control system guaranteed by the brands who, operating legally, comply with the necessary operational and regulatory rules to guarantee the health of final consumers
UNDERSTANDING RISK IN EXTENDED CHAINS
As globalization and the power of the Internet usher in new opportunities, it is becoming increasingly common for any type of business to understand the range of tools that help them protect themselves from intellectual property (IP) crime. When supply chains operate on a global scale, with different legislations, different time zones, different languages and different standards, tracking and tracing products is very complicated. The weaknesses of the supply chains are linked to poor information transparency and a lack of synchronization of systems and applications. Anti-counterfeiting helps protect corporate profits, the world of work and tax revenues, safeguarding purchases and the health of consumers. Incidentally, the increase in counterfeit drugs and personal protective equipment following the Covid-19 pandemic was yet another confirmation of the pervasiveness of the phenomenon of counterfeiting that knows no ethics and has no borders.
ANTI-COUNTERFEITING: THE AUTHORITIES AND OPERATORS INVOLVED
The problem of counterfeiting must be addressed by law enforcement authorities who must work together effectively to stem international crime. However, large and small businesses also need to maximize their protection against fakes. Today, there are numerous technological solutions that help protect property rights, supply chains, and also guarantee the authenticity of products sold online.
ANTI-COUNTERFEIT TECHNOLOGIES: WHAT THEY ARE AND WHAT THEY ARE FOR
Anti-counterfeiting technologies differ according to their functions, the ways they use to perform them, and how they are inspected. When it comes to the fight against counterfeiting, in fact, the techniques can be verified by the human senses or it is necessary to use special recognition devices. However, the common feature of all anti-counterfeiting methods is the use of specific marking devices (so-called markers). These are inextricably linked to the products (through various techniques) and contain the specific information that allows the technology to perform its essential function.
THE FUNCTIONS OF ANTI-COUNTERFEITING
From remote sensors associated with the Internet of Thing to the insertion of hidden identifiers within components and products, the markers used in the fight against counterfeiting perform one or more of the following functions:
- Authentication (through unique identification techniques)
- Track & trace (via two-dimensional codes, RFID or NFC tags and so on)
- Anti-tamper / anti-alteration (such as, for example, tamper labels and electronic seals)
GUIDE TO ANTI-COUNTERFEIT TECHNOLOGIES
From electronic identification or tracking devices, to how to place markers on products or packaging, to the use of chemical, physical and mechanical solutions, up to including digital tools, there are several ways to combat counterfeiting.
In general, anti-counterfeiting technologies provide the tools that help determine if a product is genuine or fake, or if it has otherwise been the subject of fraudulent activity.
Vericode has developed an innovative solution that aims to defend the original products of any product area from the problem of counterfeiting
In recent years, additional tools and standards have been added as add-ons such as blockchain, used in combination with other technologies to enhance overall anti-counterfeiting defenses and the new ISO standards on anti-counterfeiting technologies that provide guidelines and best practices for choosing authentication solutions.
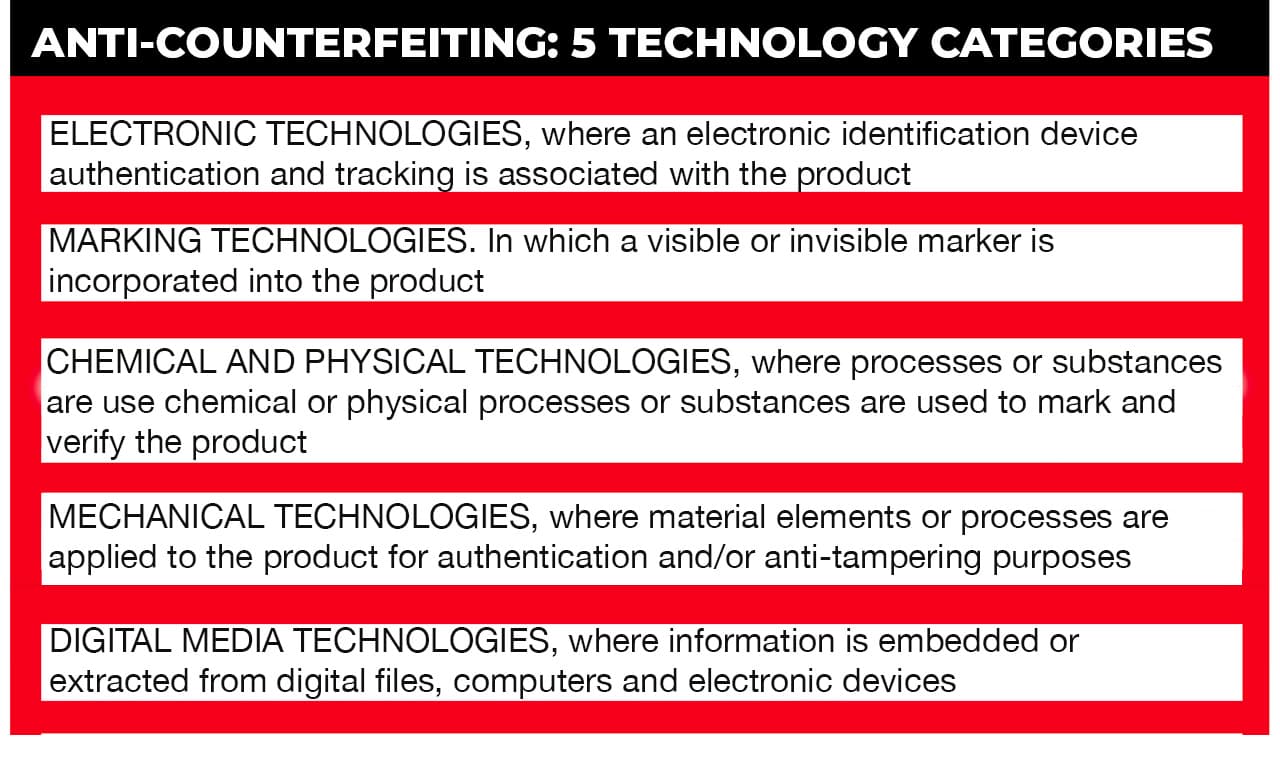
# 1 ELECTRONIC TECHNOLOGIES
Electronic anti-counterfeiting technologies all involve the association of data and goods with the aid of special electronic devices. These devices allow you to uniquely identify, authenticate and track any type of item, providing the same product specific information and / or providing access to a database where master data is stored. There are five types of solutions, but the most common are those based on radio frequency identification associated with the IoT and which perform the remote recognition of objects, vehicles, plants, animals or people. The types are listed below:
- RFID (Radiofrequency IDentification)
- NFC (Near Field Communication)
- Sensors
- Electronic seals
# 2 MARKING TECHNOLOGIES
As the name suggests, marking technologies work by marking products with unique security features, through the application of graphic models or special coding systems.
The main purpose is to authenticate rather than identify products. The security that markers provide against reproduction and tampering derives either from the nature of the technology itself (for example the chemical and physical characteristics of an ink) or from the information it contains (for example in a graphic pattern). In the first case, security is provided by a visual indication while, in the second, security derives from the difficulty of cloning or reproducing the information.
n some cases (for example in the presence of a barcode, it can constitute part or the whole of a marking technology or it can be incorporated into it) markers can support product traceability by allowing products to be registered as they move along the supply chain. There are several technologies in this area: the most used are those that can be inspected by the human eye due to their variety, low cost per item and simple verification procedures. With regards to this, in many cases the verification operation can be performed through a visual inspection by a specialist or through the use of an app enhanced by image recognition carried out via a mobile device. Below is the list of solutions:
- Optical memory bands
- Security holograms
- Microtexts
- Guilloche / random rainbow printing processes
- Unique identification markers
- Identification / detection pattern
- Watermarks
- Invisible inks
- Codes readable by automated systems
# 3 CHEMICAL AND PHYSICAL TECHNOLOGIES
Chemical and physical anti-counterfeiting technologies use special substances to mark and verify objects. By exploiting the inherent randomness of patterns produced when certain processes or chemicals are applied to materials, they act as markers. The main purpose of these technologies is authentication without simultaneous unique identification of the product, but they require the use of specialized hardware or laboratory tests to read and verify the generated markers. This makes it very difficult to reproduce similar markers by third parties. The costs for creating and affixing chemical and physical markers are generally low. However, specialized automatic reading devices, when needed, can be expensive. Therefore, it is worth remembering that immediate on-site verification is often not possible, not to mention that tests must be performed by the laboratories, which lengthens verification times. There are four types of chemical and physical technologies:
- DNA coding
- Chemical coding and tracers
- Glue Coding
- Surface analysis, chemical coding and tracers
# 4 MECHANICAL TECHNOLOGIES
Mechanical technologies work with the physical properties of materials to prevent counterfeiting and create effective tamper barriers. When used alone, they perform simple authentication functions. When used in conjunction with other technologies, they can also perform identification and tracking functions. For example, unique identification codes can be included in a label to allow product traceability.
Most mechanical solutions take the form of different types of labels, which can be classified according to their physical properties (i.e. the material used and / or how they are attached to the product). Labels usually need to be authenticated via an automatic reading device, such as a barcode reader. However, for other types of mechanical solutions, such as laser engraving, authentication can be done visually. The cost per item of mechanical solutions is generally medium-low and, in the specific case of labels, production times are very fast, as often only limited changes to the production process are required. The types are listed below:
- labels
- laser engraving
- Anti-alteration devices
- Seals
- Security films
- Security threads (of various materials such as metal, fabric or polymers) intertwined or otherwise integrated with the products to allow authentication and prevent tampering. Additional security features, such as special coatings or microprinting, can be applied to the thread for more advanced protection against counterfeiting.
# 5 ANTI-COUNTERFEITING FOR DIGITAL MEDIA
Digital media are all data presented in a machine readable format. Includes digital images, digital video, MP3 audio, e-books, video games, and databases. Anti-counterfeiting technologies designed for use with digital media essentially consist of several methods of embedding and identifying information in digital files, computers and electronic devices in order to protect, identify and track their intellectual property content. There are four types of anti-counterfeiting technologies for digital media that fall into two main categories: digital right management (DRM) systems and automatic content recognition technologies. DRM systems are designed to combat large-scale counterfeiting of audiovisual works. They are used by copyright holders and other associated rights holders to protect, exercise and manage their rights in the digital environment. Automatic content recognition technologies generally aim to identify content that is in a media file or that is being played on a device. They are developed for a variety of purposes, and intellectual property protection is just one of them. The automatic content recognition technologies that can be used to protect digital media incorporate, calculate and generate information relating to specific digital content (text, image, sound, video) that can be subsequently detected or extracted to identify its nature, origin and source. The types are listed below:
- DRM systems
- Digital watermarks
- Fingerprints
- Hashing
THE CONTRIBUTION OF THE BLOCKCHAIN TO ANTI-COUNTERFEITING
Although blockchain is still a fairly new technology, there are already some use cases in support of anti-counterfeiting. In fact, some companies create their own product IDs, monitoring supply chains. There is no single standard for using blockchain to combat counterfeiting, but examples can be found in sectors such as luxury goods, diamonds, agribusiness, electronics and pharmaceuticals.
The interesting aspect of the blockchain is that it removes the need for a pact of trust between the parties involved in a transaction and this applies to both a financial transaction and a shipment of goods. While physical transactions are based and require the mutual trust of all parties involved (e.g. in a supply chain, trust must flow in both directions between the brand owner, manufacturer, carrier, logistics operator, distributor, retailer, etc.), digital transactions that occur in a blockchain are executed quickly, securely and transparently without either party even having to know each other. This is because the operating mechanism requires that each transaction is validated by all network participants and cryptographically sealed with its own hash (an encryption algorithm) to form a new block in the chain (hence the name). Each new block also contains immutable encrypted information from the previous block, which makes blockchain transactions relatively easy to check. Since all data in a blockchain are shared among all participants, anyone can check the records and their history at any time, making it nearly impossible to cheat the system. This means that as long as the connection between the physical product and the digital transaction is strong, the blockchain can be used to track and trace ownership and authentication history of a product, detecting counterfeits at an early stage and identifying their origin. .
By triangulating anti-counterfeiting technologies, tamper-proof packaging and blockchain, companies can fight counterfeiting more intensively
HOW AND WHY A 360 ° VIEW OF ANTI-COUNTERFEITING IS NEEDED
When it comes to anti-counterfeiting technologies, it is essential to adopt a holistic approach, from the back end to the front end. In fact, it is difficult for end customers to access the information associated with product identification technologies such as RFID tags (which require special readers), tracer inks or holographic solutions (which require special recognition techniques and the aid of specialized decoding devices) used by operators at every stage of the supply chain: production, logistics and final distribution.
THERE IS NO STANDARD SOLUTION: TO EACH HIS OWN
The fight against counterfeiting is closely related to the type of product and market to which it is addressed (B2B or B2C). Each company, in fact, has different needs also conditioned by the operating methods adopted. While some technologies may be unsuitable, others may be more suitable. In other cases, it is necessary to combine different technologies to meet complex requirements and / or increase the effectiveness of law enforcement actions.
Among the solutions supporting also end consumers, today there are sophisticated but extremely intuitive solutions such as Vericode, which allow you to quickly access information related to the authenticity of a product with the certainty that these are certified and guaranteed.
VERICODE: FROM BACK END TO FRONT, ANTI-COUNTERFEITING IS TURNKEY
VeriCode is a neural network based system, which uses a neural network based artificial intelligence system to analyze suspicious events. Depending on the specific needs of the manufacturer, VeriCode is an approach characterized by great modularity and flexibility, adapting to the type of product, business and final target. Each brand can follow every single product traced along the entire supply chain, thanks to analysis and business intelligence tools capable of offering, within an easy-to-use dashboard, reports and alerts tailored to the specific needs of the business. If the product has the VeriCode label, the end customer has an alphanumeric code which, before each purchase, allows him to check if a product is authentic, allowing it to be distinguished from any non-original copy.
- Log in to post comments